Why use biostimulants in the cultivation of blueberries?

These substances are able to help achieve a harmonious growth of the plants and that they are expressed in a better way. Although they do not directly affect specific physiological events, they stimulate natural processes to improve the absorption of nutrients, the tolerance to abiotic stress and the caliber of the fruits.
In recent years, blueberries have positioned themselves as one of the crops with the greatest projection in the country. For this reason, appealing to the different tools that exist in the market to improve their development at a productive level appears as a totally logical move.
In this context, the use of biostimulants is an alternative that is gaining more followers. And is that these substances are able to help achieve a harmonious growth of plants and that these are expressed in a better way. Although they do not directly affect specific physiological events, they stimulate natural processes to improve the absorption of nutrients, the tolerance to abiotic stress and the size of the fruit, an attribute that is key in this market. In addition, in the case of new plantations, they favor greater rooting and sprouting.
At present there are several alternatives of these products in the market, which are formulated with different natural compounds. The most frequent are made from extracts of terrestrial vegetables, algae, seeds or combinations of raw materials.
Another important component in these products are amino acids, which make up proteins and are precursors of several phytohormones, chemical signals that facilitate communication between cells and coordinate their activities. In the same line, some vitamins, antioxidants, carbohydrates, and macro and micronutrients are used as complements.
"Biostimulants help to ensure greater assimilation of absorbed ammonium, provide quality amino acids, optimize photosynthesis and tissue development, promote an optimal accumulation of reserve substances and a greater cellular turgor and regulation of the development of berries" explains Henry Ibarra, Eurochilena's consultant on sustainable plant nutrition.
Characteristics of the most used compounds
For the expert, it is most appropriate that these products are used in varieties of blueberries that have dry matter levels less than 20%, in order to ensure that the fruit has a good trip and reaches its destination in excellent conditions.
1-Humic substances
They are complex and very heterogeneous organic macromolecules that are obtained with the decomposition of the organic substance and the activity of the microorganisms.
"They are a complex mixture of different acids that contain carboxylic and phenolic groups, together with sugar derivatives," says Ibarra.
They are obtained, above all, from deposits of fossil humus or compost.
"The humic substances of peat and compost with earthworms seem to have a greater biostimulating activity than those of fossil humus deposits," he says.
The application of these organic substances allows to enhance the radical development in the post-transplant phase and helps to overcome the post-transplant crisis more easily. Other advantages of these substances are that they increase the vegetative development, the foliar mass and the bioavailability of nutritive elements.
"In addition, it prevents oxidative phenomena and improves tolerance against biotic and abiotic stress, especially by salinity. Similarly, it improves soil fertility and reduces the activity of potentially phytotoxic ions, such as partner (Na +) and chlorine (Cl-), "says Henry Ibarra.
2-Algae extracts
Today there are more than 30 thousand species of algae. Those used in agriculture for the production of extracts with biostimulant action are mainly green, red or brown algae, among which are Ascophyllum nodosum, Ecklonia maximum, Laminaria digitata and Fucus. These are collected manually or mechanically on the oceanic coasts of Canada, South Africa, Ireland and China.
"The extraction can be of different forms and occupying solvents of different nature. The most widely used method involves cold extraction in high pressure water to prevent chemical alterations of bioactive molecules ", explains Eurochilena's advisor.
The biostimulant effect of these algae is due to the activation of the biosynthetic pathways of the hormones in the plant rather than to an external contribution. Depending on the type of species, he adds, the presence of some compounds is prevalent.
"Above all, the polysaccharides mannitol, laminarin, alginates, fucoidanes, important for their stimulation in the absorption of nutrients and in the improvement against the environmental stress of plants," explains Ibarra.
With the use of these extracts an increase in the speed of germination and a stimulus for the multiplication and cellular distension, of the fruit set is achieved. In the same way, a growth of the osmolytes accumulation is achieved, which stabilizes the cellular membranes (maintaining cellular turgor and reducing the activity of the free radicals that destroy the cells) and the activity of the defense enzymes against oxidative stress .
This translates into benefits such as an increase in the size of the fruits, resistance against biotic stress (mold, rot, mites, aphids, nematodes) and abiotic (drought, salinity and extreme temperatures) and greater vegetative development, among others.
3-Betaínas
"Betaines are natural substances that are extracted from sugar beets (beta vulgaris). They are compounds that plants accumulate naturally in response to environmental stress in cases of high and low temperatures, drought or salinity of the land, "Ibarra said.
He adds that the intracellular accumulation of these substances allows the water retention in the cells, protecting them against the effects of dehydration, "without disturbing the enzymatic function, the structure of the proteins and the integrity of the membrane".
To improve the hydric state of the plants, to quickly favor the overcoming of the hydric and saline stress, to reduce it during the ripening of the fruits, to allow an increase of the shelf life and to maximize the sugar degree and the qualitative characteristics of the productions, are its main effects.
4-Hydrolysates of proteins
The main advantage is that they positively stimulate all the processes of the most important primary metabolism, such as photosynthesis and the synthesis of DNA and proteins; and secondary, such as resistance against stress, the maturation of fruits and the absorption of nutrients.
"These are products based on amino acids and soluble peptides normally obtained by chemical, enzymatic or mixed hydrolysis of proteins of animal or vegetable origin", explains the agronomist. It should be noted that amino acids are the basic components of proteins, complex macromolecules that in the plant develop structural, enzymatic and hormonal functions.
Ibarra explains that while protein hydrolysates with collagen have, especially, glycine and proline; those of Fabaceae contain glutamic acid, aspartic acid and tryptophan, which operates as an important precursor of auxin biosynthesis in plants.
"Protein hydrolysates obtained enzymatically are characterized by having a much higher percentage of free amino acids in levogy (vegetable) form, which are effectively used by plants. With enzymatic hydrolysis the percentage of free amino acids is 90%, while with chemical hydrolysis it does not exceed 50%, "says Ibarra.
The protein hydrolysates, in addition, improve the absorption and assimilation of nutrients; they influence the growth of plants indirectly, stimulating the telluric microflora; and favor the presence in the final product of a higher content of antioxidants and proteins and a lower nitrate content.
5-Triacontanol
It helps plants to perform at their best, even in situations of stress. Triacontanol is a long-chain alcohol (of 30 C atoms) that is part of the family of policosanols (aliphatic alcohols) present in nature, specifically in the cuticular waxes of plants and in beeswax.
Aliphatic alcohols are extracted from sugar cane, some by-products of the processing of cereals (wheat germs) and other plants, among which are the Fabaceae, and Guar flour.
"Among the extraction methods used, the enzymatic hydrolysis of the Fabaceae (which contains a lot) is the one that manages to extract triacontanol more efficiently, obtaining products with a content always higher than 6mg / kg and natural," says Henry Ibarra.
Its use has a radiant effect in the post-transplant phase. In addition, it increases the vegetative development, the sugar content and the fruit set. It also reduces the accumulation of nitrates in the leaf and strengthens the tolerance against salinity and biotic stress.
6-Polysaccharides
The polysaccharides used in the field can be extracted from different plant species, such as algae and almost all higher plant species.
"But they can also be extracted from industrial processing waste. The main sources for the preparation of biostimulants are algae, vinasse and molasses, "warns Ibarra.
These substances, in addition to fulfilling a nutritional function, have other roles, such as supplying the plant with organic carbon and energy available immediately for photosynthesis and primary metabolism.
"They also create the conditions so that the nutritional state helps the plant in its growth and that it is greener and stronger," adds Ibarra.
Similarly, some polysaccharides such as laminarin, alginates and fucoidans are important, because they improve the tolerance against environmental stress of plants.
Another of its effects is that they regulate the development of the phases of maturation of the fruits, and increase the degree of sugar in the berries and the time of conservation in showcase, especially in the climacteric fruits, which are able to continue maturing once separated. of the plant.
Triacontanol and amino acids in action
According to an assay carried out by ILSA in four different locations, the application of triacontanol and amino acids in the varieties Blue Gold and Ochlockonee, allows to improve the firmness of the berries in harvest and post-harvest.
The study was carried out in blueberry crops located in Santa Fe and Los Angeles (Biobío), and in Cato and San Nicolás (Ñuble). In total, four applications of 1 L / ha of Triacontanol (6ppm) plus amino acids (5,7% Aa total) were made every 15 days, starting at 50% of fruit set. The measurements were taken on the day of harvest, at the 15 and 30 days of post-harvest, in a Soft Sorter of BBC Thechnologies.
The trial of the Blue Gold variety carried out in Santa Fe showed the best results. If on the day of harvest the control group yielded 103 gr / mm displacement, the area where biostimulant was applied showed 224 gr / mm displacement.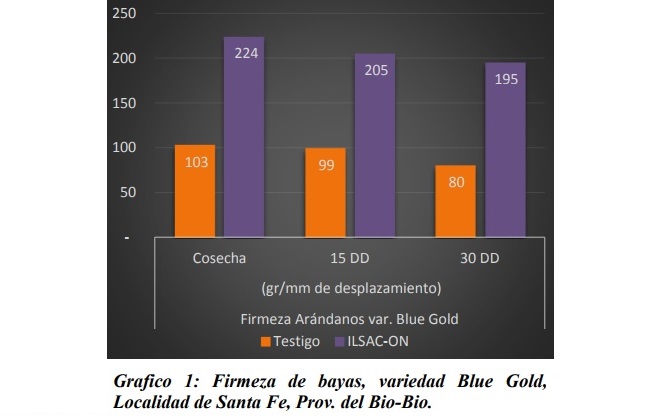
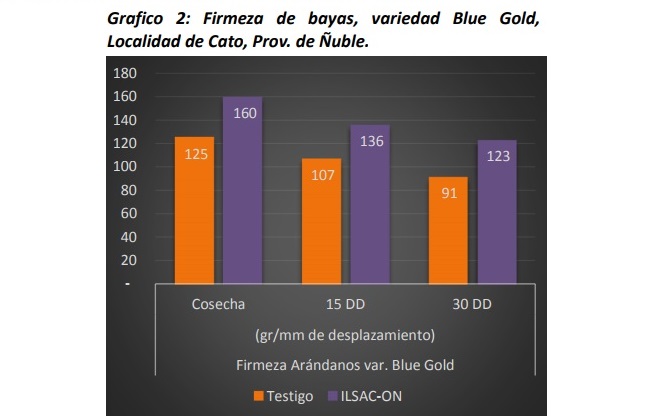
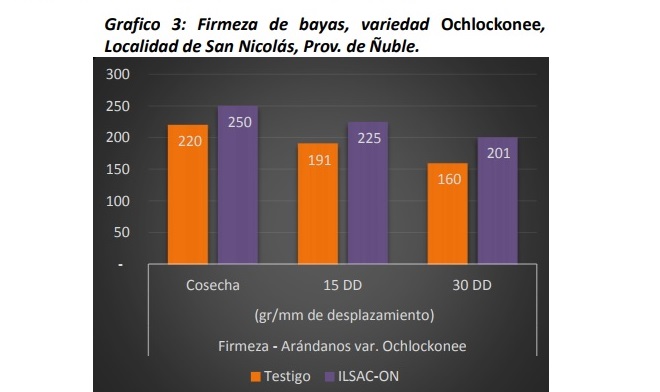
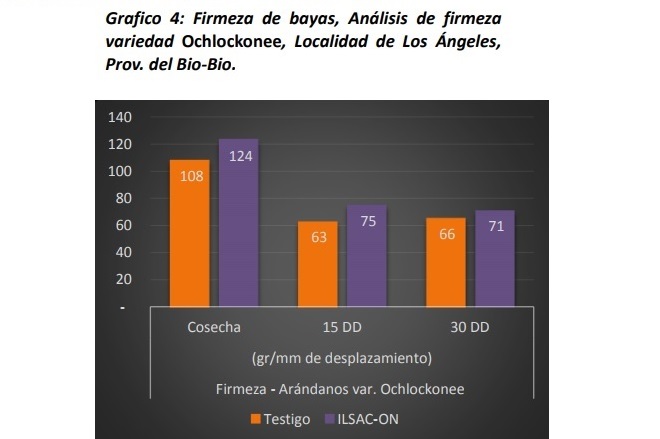
Source: elmercurio.com
Previous article
The blueberries from Tucumán, a little closer to Chinanext article
Chile is the destination of Peruvian blueberries








